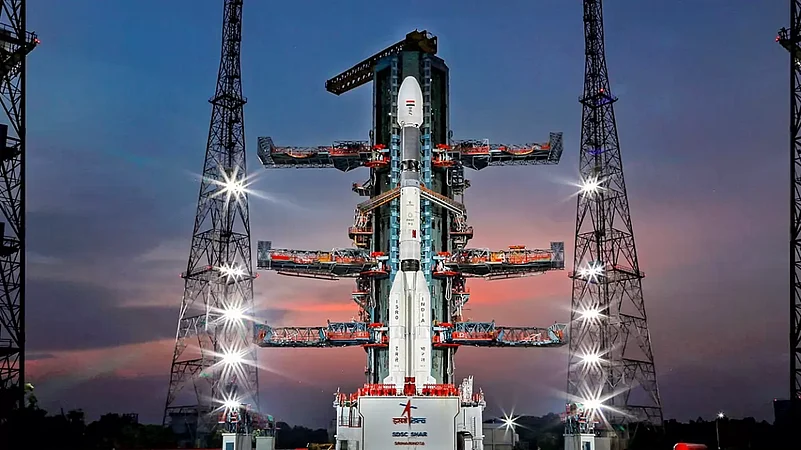
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on Monday launched the second-generation navigation satellite NVS-01 on board a GSLV rocket from Sriharikota spaceport. Amid clear skies, it took off at a prefixed time of 10.42 am.
The second-generation navigation satellite series is a significant launch which would ensure the continuity of NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) services -- an Indian regional satellite navigation system, similar to GPS, providing accurate and real-time navigation in India and a region extending to 1,500 km around the mainland.
What is NavIC?
The Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) is a regional navigation satellite system developed by ISRO that is a constellation of seven satellites in orbit that work alongside ground stations. It offers two services -- Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and Restricted Service for strategic users. NavIC SPS signals are interoperable with the US global navigation satellite system signals, GPS, Glonass from Russia, Galileo (European Union) and BeiDou, China.
ISRO developed the NavIC system to meet the positioning, navigation and timing requirements of the country, particularly with regard to civil aviation and military requirements. NavIC was earlier known as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS).
"The L1 navigation band is popular for providing position, navigation and timing services for civilian users and for interoperability with other GNSS (global navigation satellite system) signals," ISRO said.
Some of the applications of NavIC include terrestrial, aerial and maritime navigation, precision agriculture, location-based services in mobile devices and marine fisheries, among many others.
NavIC signals are designed to provide user position accurate to better than 20-metres and timing accuracy better than 50 nanoseconds. The 51.7 metre tall Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle, on its 15th flight, would carry the navigation satellite NVS-01 weighing 2,232 kg on Monday at 10.42 am from the second launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SHAR) here, about 130 km from Chennai.
Nearly 20 minutes after the flight, the rocket is scheduled to deploy the satellite in a geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO) at an altitude of about 251 km, ISRO said. The NVS-01 carries navigation payloads L1, L5 and S bands and in comparison with the previous one, the second-generation satellite would also carry an indigeneously developed rubidium atomic clock.
It is for the first time that an indigeneously developed rubidium atomic clock would be used in Monday's launch, ISRO said. According to the space agency, scientists earlier used imported rubidium atomic clocks to determine date and location. Now, the rubidium atomic clock developed by Ahmedabad-based Space Applications Centre will be on board. It is an important technology that only a handful of countries possess, it said.
Monday's mission is the sixth operational flight of the GSLV with indigenous cryogenic stage. The mission life of NVS-01 is expected to be better than 12 years, ISRO said.
(With inputs from PTI)