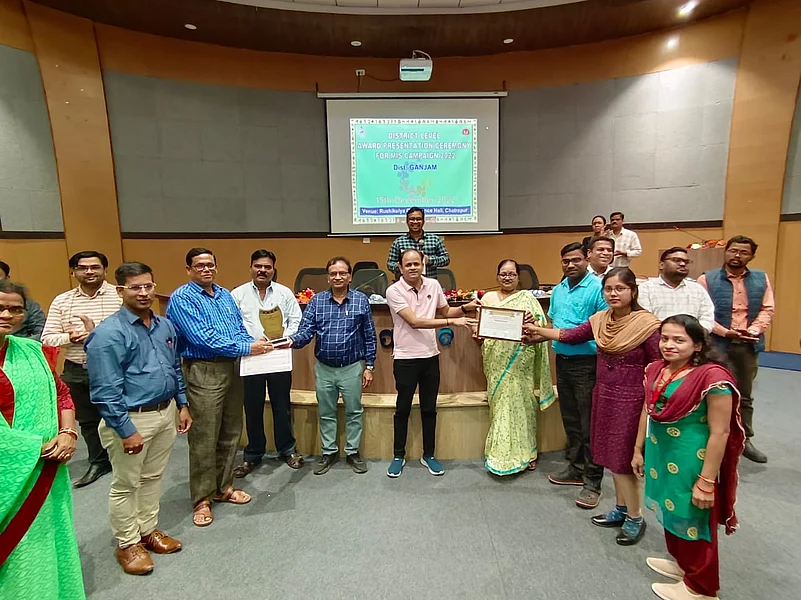
In a remarkable display of community engagement and public health initiatives, Odisha's Ganjam district has emerged as the state leader in implementing the 'Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan' (Prime Minister's TB-Free India Campaign). The district has successfully facilitated the adoption of all its registered tuberculosis (TB) patients, setting a benchmark for other regions to follow.
The Tuberculosis Challenge in India and Odisha
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant public health challenge in India, with the country accounting for about a quarter of the global TB burden. According to the India TB Report 2023, the country reported 21.4 lakh TB cases in 2022, a 13% increase from the previous year. In Odisha, the situation is particularly concerning, with the state reporting 52,470 TB cases in 2022. The state faces unique challenges in TB control due to its diverse geography, ranging from coastal regions to tribal areas, which can affect healthcare access and treatment adherence. Despite these challenges, Odisha has shown commitment to TB eradication, with a treatment success rate of 83% for new and relapse cases. It's against this backdrop that the success of Ganjam district in implementing the 'Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan' gains particular significance.
Program Overview
The 'Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan', launched by the Central Government in September 2022, aims to eradicate tuberculosis in India. A key feature of this program is the concept of 'Ni-kshay Mitra' or donors, who can adopt TB patients and provide them with nutritional and treatment support.
Dr. Abani Kumar Patra, the district TB officer, proudly announced that Ganjam has topped the state in patient adoption. "As many as 540 individuals and organizations in Ganjam district have adopted all 3,779 TB patients under the scheme," Dr. Patra stated, highlighting the district's comprehensive coverage.
Community Participation
The success of the program in Ganjam can be attributed to wide-ranging community participation. The scheme allows various entities to become Ni-Akshay Mitra, including:
Individuals
Institutions
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs)
Cooperative societies
Elected representatives
Political parties
Other partners
These donors can adopt blocks, districts, or even individual TB patients, providing much-needed support in the fight against tuberculosis.
Nutritional Support
The program coordinator, Bideshi Jena elaborated on the nutritional aspect of the support provided. “The patients are not provided with any kind of cash but instead monthly food kits are provided to them.
The monthly food kit, valued at approximately Rs 700 to Rs 800 per patient, includes:
3 kg cereals and millets
1.5 kg pulses
1 kg milk powder
250 grams of vegetable oil and cooking oil
Jena also mentioned that non-vegetarian food options are available for those willing to provide them. The adoption period can range from six months to three years, allowing for sustained support throughout the treatment process.
Recognition and Awareness
To mark the second anniversary of the scheme, coinciding with Prime Minister Narendra Modi's birthday, the district health administration organized a special meeting. Dr. SK Padhy, the Chief District Medical Officer, said the event was held to felicitate the Ni-kshay Mitra and create awareness about the scheme.
During the meeting, some of the donors were felicitated for their contributions. Dr. Padhy used this platform to urge more people to come forward and adopt patients by providing nutritional support.
Looking Ahead
Indeed, the success of Ganjam district in the implementation of the 'Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan” is an inspiring model for other areas and states. The adoption of all the reported 3,779 TB patients is a noteworthy success of a positive initiative. Ganjam has shown the power of community engagement in public health initiatives.
This achievement is particularly significant given India's substantial TB cases, with 21.4 lakh cases reported in 2022, and Odisha's differentiated challenges in TB control. Ganjam's approach aligns with Odisha's commitment to TB eradication, which has already yielded an 83% treatment success rate for new and relapse cases.
As the program continues to grow, this collaborative approach could significantly help with India's goal of becoming tuberculosis-free. The Ganjam model showcases how local action can drive national health objectives, potentially transforming TB treatment and prevention across the country.